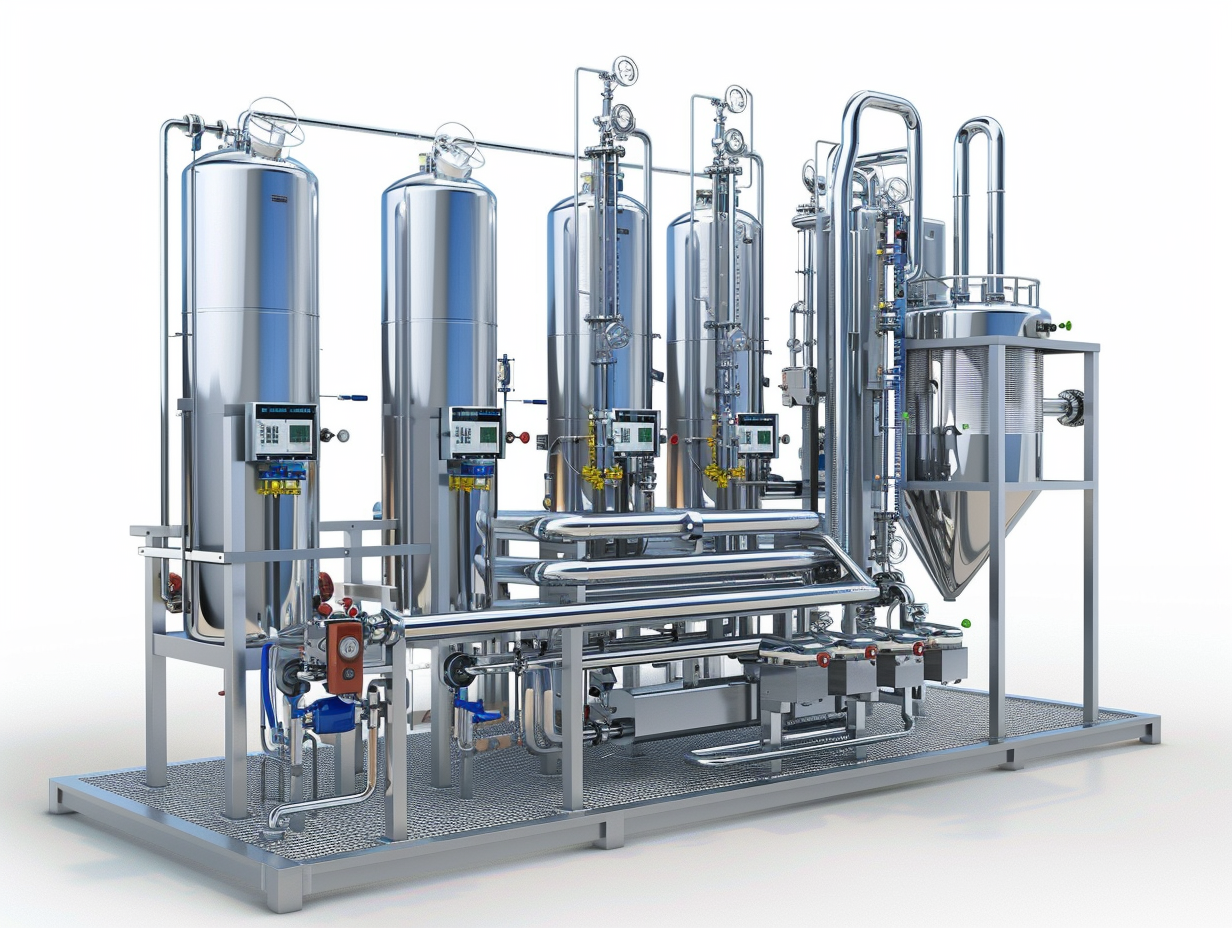
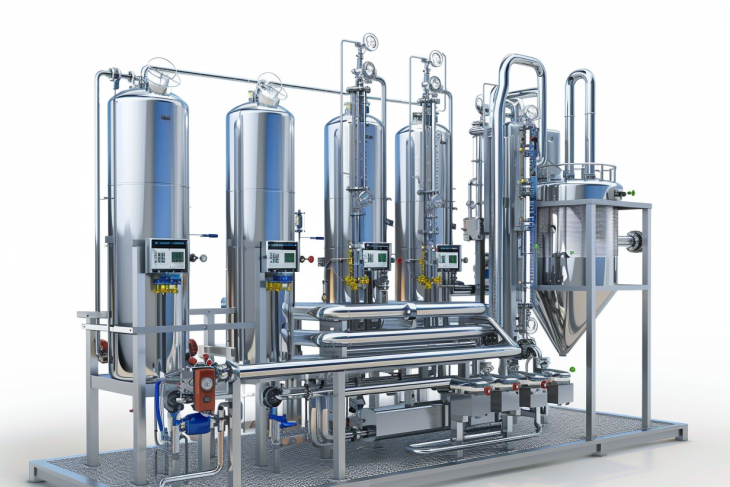
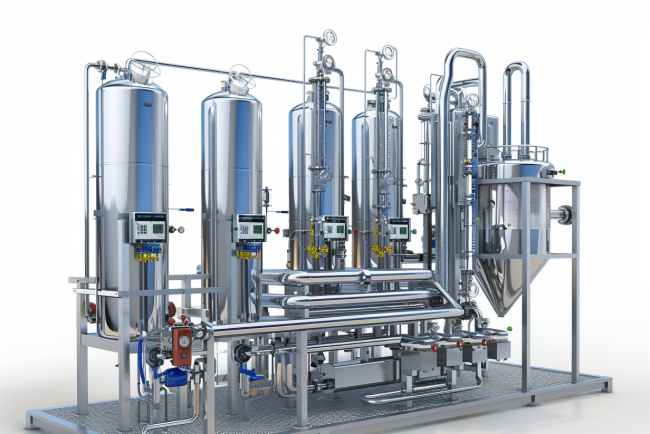
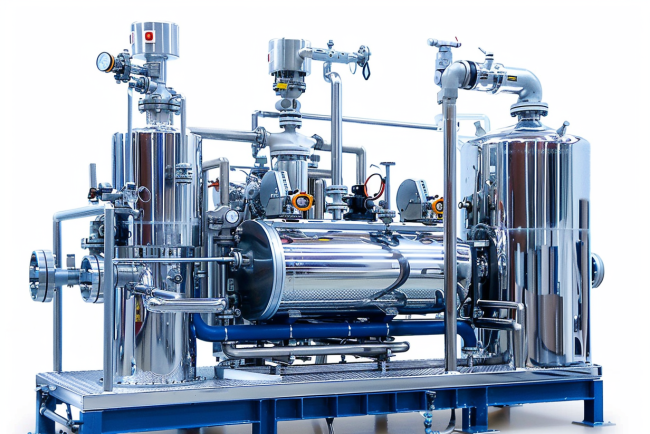
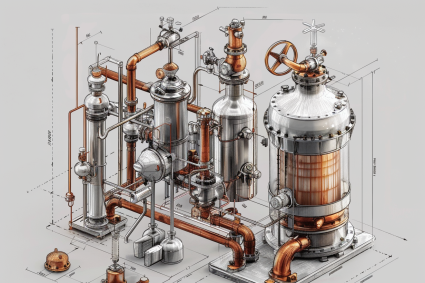
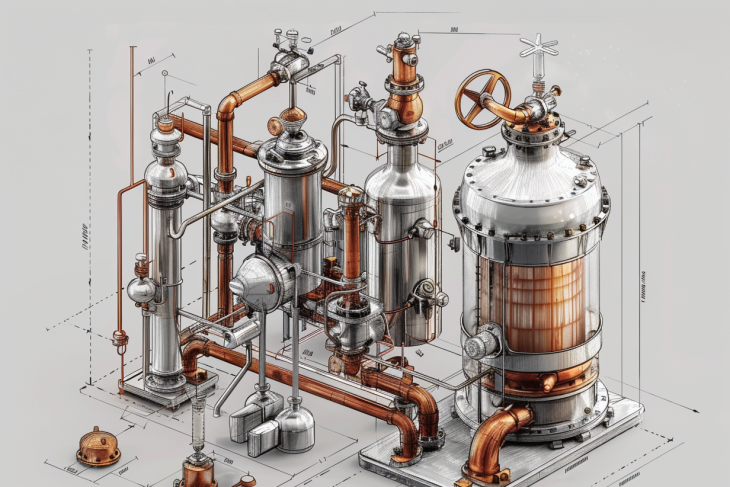
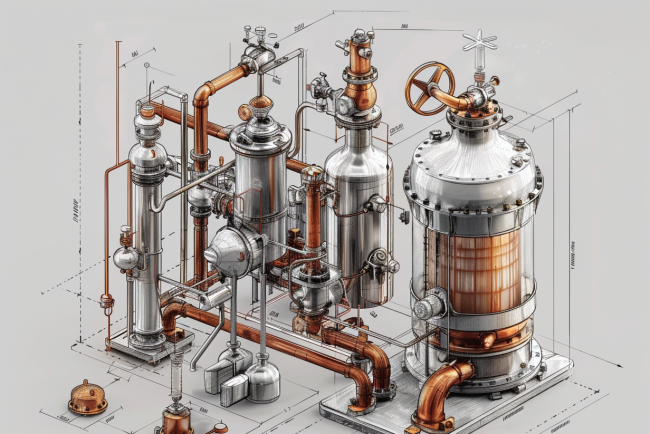
Understanding the Triple Effect Evaporator
A triple effect evaporator is a type of multiple effect evaporator system designed to optimize the efficiency of the evaporation process by utilizing three stages or effects. Each effect utilizes the vapor generated in the previous stage to heat the next stage, thereby significantly reducing the overall steam consumption and enhancing energy efficiency. This system is widely used in various industries to concentrate solutions efficiently.

A triple effect evaporator capitalizes on the principle of sequential vapor usage across three stages, improving energy efficiency by utilizing the vapor from one stage to heat the subsequent stage.
Working Principle of a Triple Effect Evaporator
1. Introduction of Feed Solution
The feed solution, which needs to be concentrated, is introduced into the first effect (stage) of the evaporator system. Each stage comprises an evaporator vessel, heat exchanger, and other essential components.
2. Steam Supply to the First Effect
Steam is provided to the first effect, where it serves as the heat source. The heat from this steam causes the solvent (typically water) in the feed solution to evaporate.
3. Vapor Reuse for Heating Subsequent Effects
The vapor generated in the first effect is then used as the heating medium for the second effect. This process continues:
- First Effect: Vapor heats the feed solution, causing the solvent to evaporate.
- Second Effect: Vapor from the first effect is used to heat the second effect, where further evaporation occurs.
- Third Effect: Vapor from the second effect heats the third effect, resulting in additional evaporation.
4. Sequential Evaporation and Pressure Gradients
Each effect operates at progressively lower pressures and temperatures. The pressure gradient ensures that the vapor from one effect has sufficient energy to evaporate the solvent in the subsequent effect.
5. Final Vapor Condensation
In the third and final effect, the remaining vapor is condensed using cooling water or other methods. The solvent is collected, and the concentrated solution is drawn off from the evaporator system.
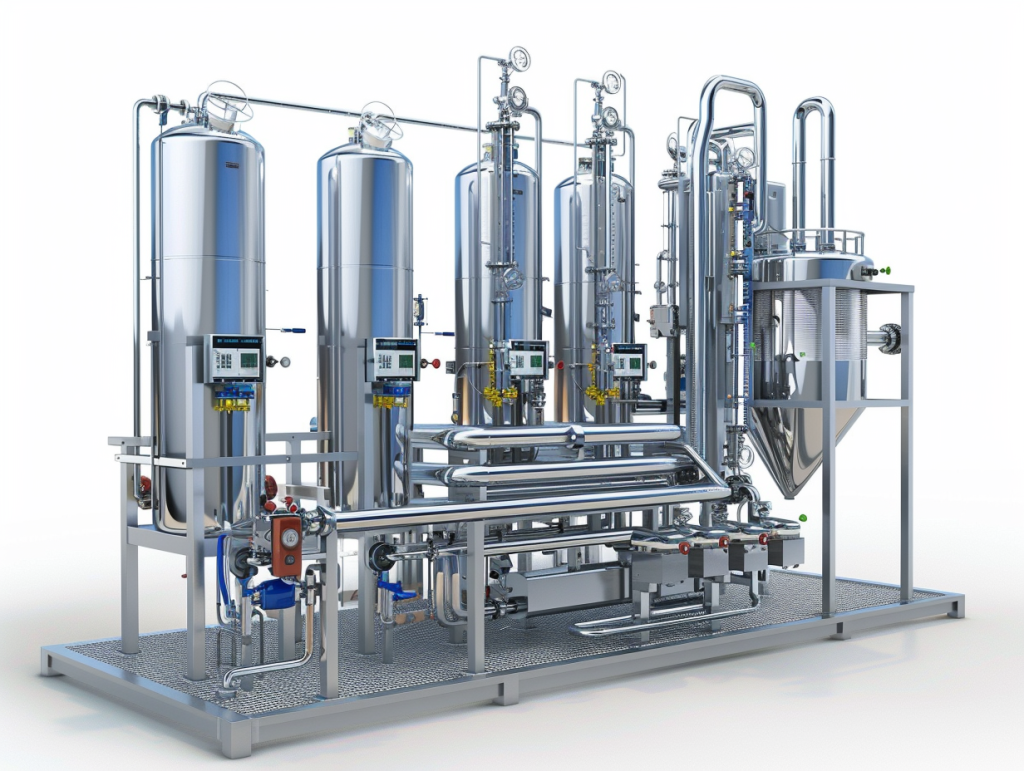
Components of a Triple Effect Evaporator
1. Evaporator Vessels
Each effect includes an evaporator vessel where the feed solution is heated, and evaporation occurs. These vessels are designed to operate under specific pressure and temperature conditions.
2. Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers facilitate the transfer of heat from the vapor of one effect to the feed solution in the next effect, ensuring efficient heat exchange.
3. Vacuum System
A vacuum system is utilized to maintain the lower pressure in the subsequent effects, optimizing the evaporation process and maintaining the necessary temperature gradients.
4. Condenser
The condenser is used to condense the vapor from the final effect back into the liquid solvent. Effective condensation is essential for maintaining the system’s overall efficiency.
5. Steam Trap and Separator
Steam traps and separators ensure that only vapor is used for heating subsequent stages, preventing liquid carryover and optimizing the evaporation process.
Advantages of a Triple Effect Evaporator
1. Improved Energy Efficiency
Triple effect evaporators enhance energy efficiency by reusing vapor from one effect to heat the next, reducing the need for fresh steam and lowering operational costs.
2. Reduced Operational Costs
The decreased steam consumption results in lower fuel and utility costs, making the operation more cost-effective compared to single effect systems.
3. Environmentally Friendly
By increasing energy efficiency and reducing steam usage, triple effect evaporators have a lesser environmental impact, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and better energy conservation.
4. Scalable and Versatile
Triple effect evaporators can handle large volumes and are scalable for various industrial processes. They offer flexibility in operation and can be adapted to different types of feed solutions.
5. Enhanced Process Control
The multi-stage design allows for more precise process control, enabling adjustments to optimize performance and efficiency, essential for industries with stringent specifications.
Applications of Triple Effect Evaporators
1. Food and Beverage Industry
- Juice and Syrup Concentration: Efficiently concentrating fruit juices and syrups while maintaining flavors and nutritional properties.
- Dairy Processing: Used for concentrating milk and whey.
2. Chemical Industry
- Chemical Concentration: Ideal for concentrating various chemical solutions and recovering solvents.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Active Ingredient Concentration: Essential for concentrating active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) efficiently.
4. Wastewater Treatment
- Effluent Reduction: Reducing the volume of industrial wastewater by removing water content, making the effluent easier to manage and dispose of.
5. Desalination
- Water Purification: Used in desalination plants to concentrate saltwater and recover freshwater.
Factors Affecting the Performance of Triple Effect Evaporators
1. Feed Solution Properties
The physical and chemical properties of the feed solution, including viscosity, boiling point elevation, and thermal sensitivity, impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the evaporation process.
2. Heat Exchanger Design
The design and material of the heat exchangers affect the heat transfer efficiency and overall performance of the evaporator system.
3. Operating Conditions
Maintaining the appropriate pressure and temperature gradients across the effects is crucial for optimal performance. Deviations can impact efficiency and output.
4. Maintenance and Fouling
Regular maintenance and monitoring for fouling (build-up on heat exchange surfaces) are necessary to ensure continuous and efficient operation. Fouling can reduce heat transfer efficiency and increase energy consumption.
Conclusion
A triple effect evaporator is a multiple effect evaporator system that utilizes three stages to maximize energy efficiency by reusing the vapor generated in each stage to heat the subsequent stage. This design significantly reduces steam consumption and operational costs, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including the food and beverage industry, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, wastewater treatment, and desalination.
Understanding the working principle, components, advantages, and applications of triple effect evaporators can help in selecting the right system for specific needs, ensuring optimal performance, energy conservation, and cost-effectiveness.
FAQ
- What is a triple effect evaporator?
A triple effect evaporator is a multiple effect evaporator system with three stages, utilizing vapor from one stage to heat the next, thereby maximizing energy efficiency and reducing steam consumption. - How does a triple effect evaporator work?
It works by introducing the feed solution into the first stage, heating it to evaporate the solvent, then using the vapor from each stage to heat the subsequent stage, progressively reducing steam consumption. - What are the advantages of using a triple effect evaporator?
Advantages include improved energy efficiency, reduced operational costs, lower environmental impact, scalability, versatility, and enhanced process control. - In what industries are triple effect evaporators commonly used?
They are used in the food and beverage industry, chemical industry, pharmaceutical industry, wastewater treatment, and desalination. - What factors influence the performance of triple effect evaporators?
Factors include the properties of the feed solution, heat exchanger design, operating conditions, and regular maintenance to prevent fouling.