Introduction to Centrifugal Compressors
Centrifugal compressors are a type of dynamic compressor that utilize a rotating impeller to increase the velocity of a gas. This increase in velocity is then converted into an increase in pressure. These compressors are widely used in various industries, including HVAC, petrochemical, and power generation, due to their ability to handle large volumes of gas at high pressures. Understanding the components of a centrifugal compressor is crucial for anyone involved in the design, operation, or maintenance of these machines.

The Three Main Components of a Centrifugal Compressor
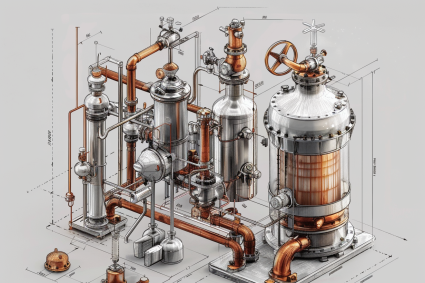
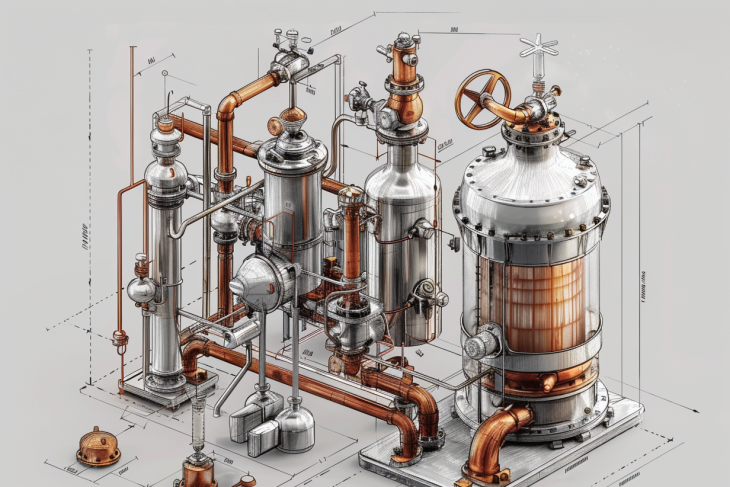
A centrifugal compressor consists of three primary components: the impeller, the diffuser, and the volute. Each of these components plays a critical role in the compression process, and understanding their functions can help in diagnosing issues and optimizing performance.
1. Impeller
The impeller is the heart of the centrifugal compressor. It is a rotating disk with blades that accelerate the gas outward from the center of rotation. The impeller’s primary function is to impart kinetic energy to the gas. As the gas enters the impeller at the eye (center), it is accelerated radially outward by the rotating blades. This acceleration increases the velocity of the gas, which is a critical step in the compression process.
**Key Features of the Impeller:** – **Blades:** The blades are designed to maximize the efficiency of energy transfer from the impeller to the gas. They can be backward-curved, radial, or forward-curved, each with its advantages and specific applications. – **Material:** Impellers are typically made from high-strength materials like stainless steel or titanium to withstand the high stresses and corrosive environments often encountered in industrial applications. – **Speed:** The rotational speed of the impeller is a critical factor in determining the compressor’s performance. Higher speeds generally result in higher pressure ratios but also require more robust materials and precise engineering.
2. Diffuser
The diffuser is the component that surrounds the impeller and serves to convert the kinetic energy of the gas into pressure energy. As the high-velocity gas exits the impeller, it enters the diffuser, where the cross-sectional area gradually increases. This increase in area causes the gas to decelerate, converting its kinetic energy into static pressure.
**Key Features of the Diffuser:** – **Shape:** The diffuser can be vaned or vaneless. Vaned diffusers have stationary blades that guide the gas flow, while vaneless diffusers rely on the natural expansion of the gas. – **Efficiency:** The design of the diffuser significantly impacts the overall efficiency of the compressor. A well-designed diffuser minimizes losses and maximizes the pressure recovery. – **Material:** Like the impeller, diffusers are often made from high-strength materials to withstand the operational stresses and corrosive environments.
3. Volute
The volute, also known as the casing, is the outer shell that collects the compressed gas from the diffuser and directs it to the discharge point. The volute is designed to manage the flow of gas efficiently and to minimize pressure losses.
**Key Features of the Volute:** – **Shape:** The volute typically has a spiral shape that gradually increases in cross-sectional area. This design helps to evenly distribute the gas flow and maintain a constant velocity. – **Material:** The volute is usually made from robust materials like cast iron or steel to withstand high pressures and temperatures. – **Function:** In addition to directing the gas flow, the volute also serves as a structural component, housing the impeller and diffuser and providing support for the bearings and seals.
Conclusion
Understanding the three main components of a centrifugal compressor—the impeller, diffuser, and volute—is essential for anyone involved in their operation or maintenance. Each component plays a crucial role in the compression process, and their design and material choices significantly impact the compressor’s performance and efficiency. By focusing on these components, engineers and technicians can better diagnose issues, optimize performance, and ensure the reliable operation of centrifugal compressors in various industrial applications.